COMPUTER VISION
Multi-level Distance Regularization for Deep Metric Learning
김용현(카카오엔터프라이즈), 박원표(카카오)Association for Advancement of AI (AAAI)
2021-02-02
딥러닝 기반 거리 학습(DMLDeep Metric Learning)은 주어진 두 데이터 간 의미적인 거리pairwise distance를 학습하는 방법입니다. 특히 입력 이미지와 유사한 이미지를 찾는 데 효과적인 이 기술은 이미지 검색image retrieval, 상품 추천, 얼굴 인식face recognition과 같은 태스크에서 핵심적으로 활용되고 있습니다.
선행 연구에서는 같은 범주의 이미지 간 거리는 더 가깝게, 범주가 다른 이미지의 거리는 더 멀게 만드는 손실 함수loss function 재정의에 집중했습니다. 다만 거리가 아닌 임베딩 벡터embedding vector를 제약하는 L2 정규화L2 normalization1로는 직접적인 거리 정규화가 어려워서 모델이 쉽게 과적합overfitting2되는 문제가 있었습니다.
이에 공동 연구팀은 DML에 더 적합한 새로운 거리 정규화 기법인 MDRMulti-level Distance Regularization을 제안했습니다. MDR은 데이터 간의 거리 분포를 여러 부분으로 나눈 뒤 각 부분을 대표하는 레벨level을 학습하고, 각 레벨에 속하는 두 쌍의 데이터 간 거리를 정규화합니다. MDR는 기존 손실 함수와 함께(jointly) 동작하며 쉬운 샘플3이 학습에 영향을 주지 못하거나 어려운 샘플4이 학습을 지배하는 현상을 방지합니다.
트리플릿 손실 함수Triplet loss function에 MDR을 적용해본 결과, 주요 벤치마크 데이터셋에서 유의미한 성능 향상을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
카카오엔터프라이즈는 이번 연구로 얻은 기술력과 경험을 바탕으로 상품 추천, 얼굴 인식 등 관련 기술을 고도화할 계획입니다.
☛ Tech Ground 데모 페이지 바로 가기 : 얼굴 검출 데모
Overall Architecture
At first, MDR normalizes pairwise distances among the embedding vectors of a mini-batch, with their mean and standard deviation to obtain the objective degree of similarity between a pair by considering overall distribution. MDR defines the multiple levels that represent various degrees of similarity for pairwise distances, and the levels and the be- longing distances are trained to approach each other (Figure 1b). A conventional loss function of DML struggles to optimize a model by overcoming the disturbance from the proposed regularization. Therefore, the learning process succeeds in learning a model with a better generalization ability.
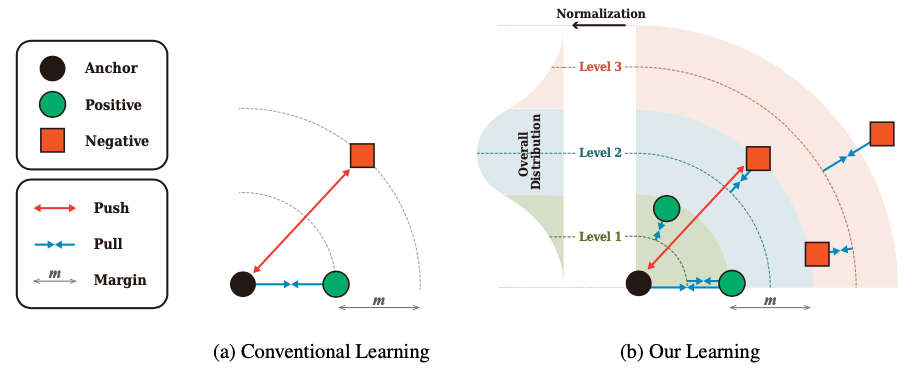
[ Figure 1 ] Conceptual comparison between the conventional learning scheme and our learning scheme. (a) illustrates the triplet learning, which is one of the representative conventional learning. It increases the relative difference between distances of a positive pair and that of a negative pair more than margin m. (b) illustrates our learning combined with the triplet learning. It has multiple levels with disjoint intervals to reflect various degrees of similarity between pairs. It disturbs the learning procedure to construct an efficient embedding space by preventing the pairwise distances from deviating from its belonging level.
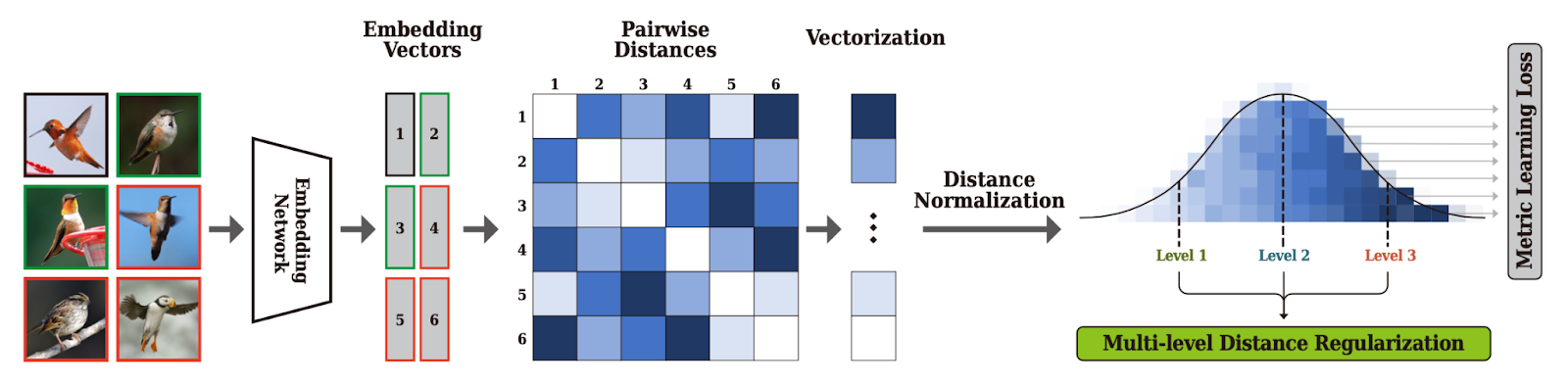
[ Figure 2 ] Learning procedure of the proposed MDR. The embedding network generates embedding vectors from given images. Our MDR computes a matrix of pairwise distances for the embedding vectors, and then, the distances are normalized after vectorization. In our learning scheme, a model is trained by simultaneously optimizing the conventional metric learning loss such as Triplet loss (Schroff, Kalenichenko, and Philbin 2015) and the proposed loss, which regularizes the normalized pairwise distances with multiple levels.
Experiments
We employ the four standard datasets of deep metric learning for evaluations: CUB-200-2011 (CUB-200), Cars-196, Stanford Online Product (SOP) and In-Shop Clothes Retrieval (In-Shop). Our method significantly outperforms the other state-of-the-art methods in all recall criteria for all datasets.
We prove the effectiveness of MDR by showing the improvements that greatly exceed the existing methods, and by extensively performing the ablation studies of its behaviors. By applying our MDR, many methods can be significantly improved without any extra burdens at inference time.
Moreover, our extensive ablation studies show that MDR can be adopted to any backbone networks and any distance-based loss functions to improve the performance of a model.
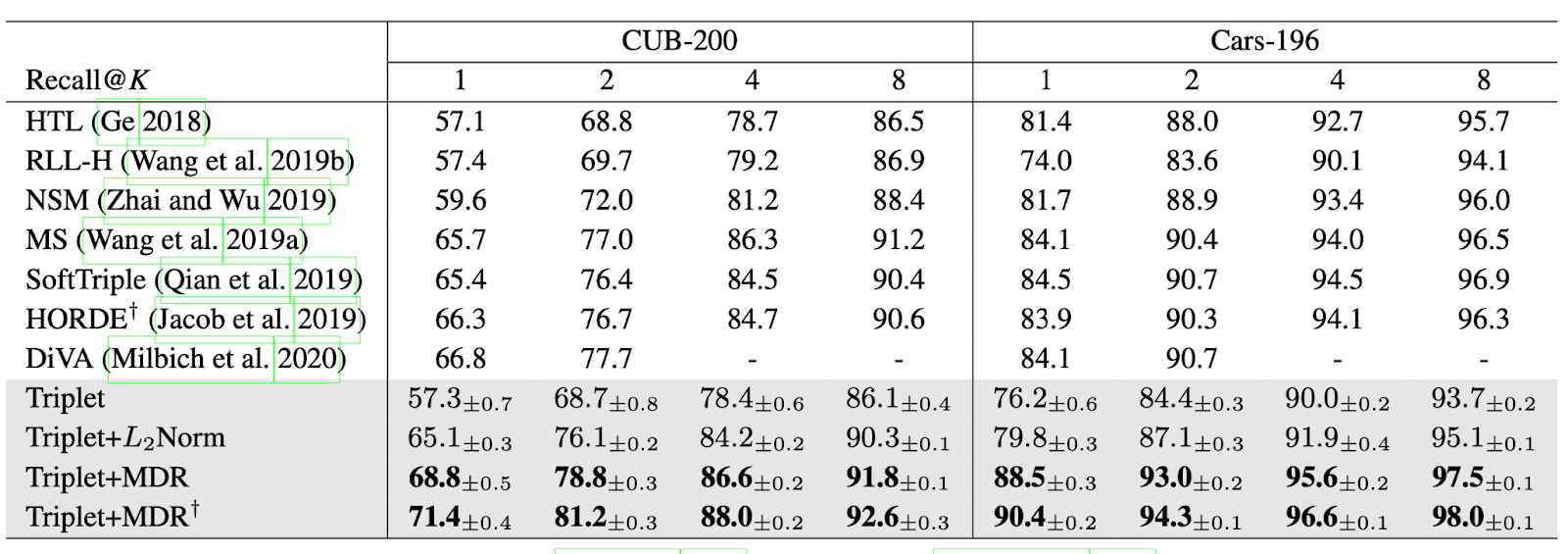
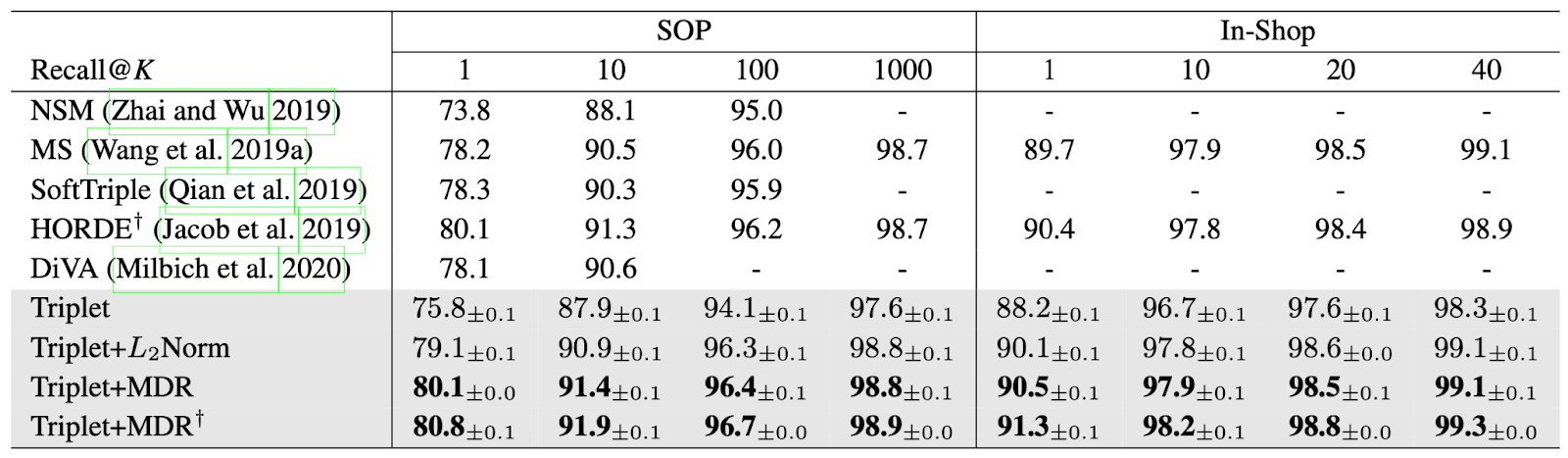
[ Table 1 ] Recall@K comparison with state-of-the-art methods. The baseline methods and MDR are grouped in the gray-colored rows. † indicates that the model is trained and tested with large images of 256 × 256 following the setting of (Jacob et al. 2019). We round reported values to the first decimal place.
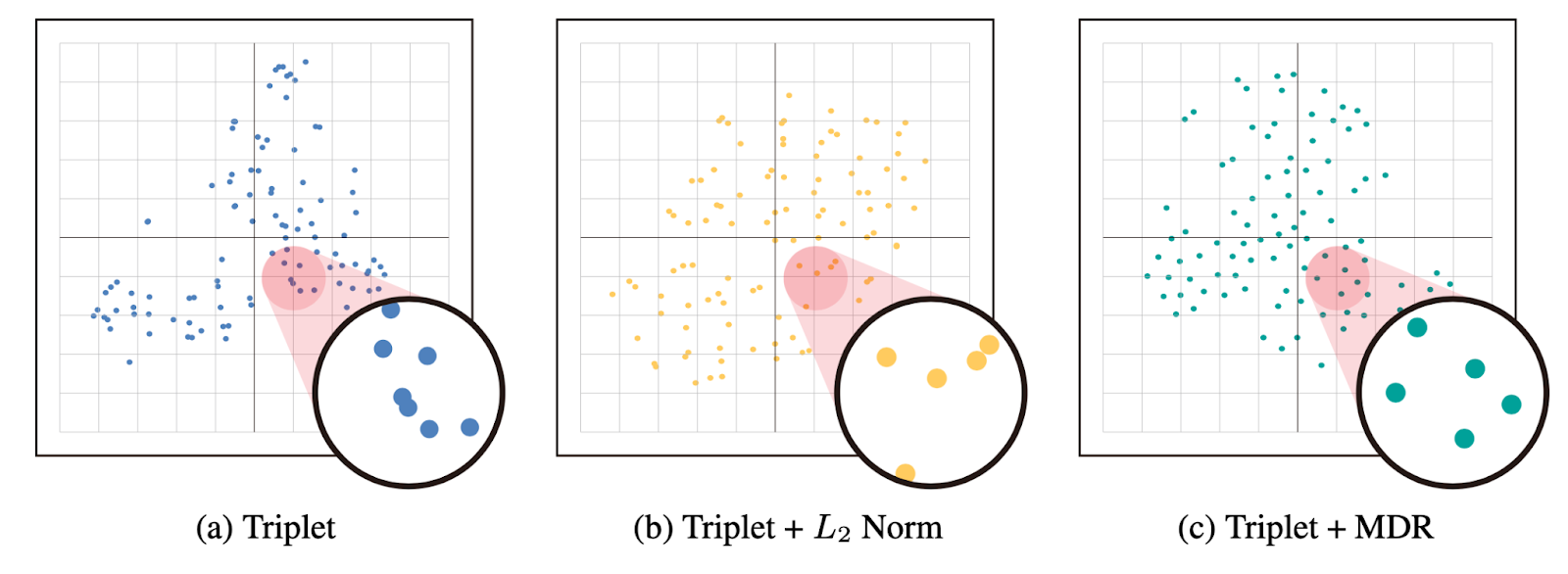
[ Figure 3 ] Class centers in the embedding space of two models trained without MDR (Triplet & Triplet+L2 Norm) and one model trained with MDR (Triplet+MDR). We visualize using t-SNE on CUB-200.
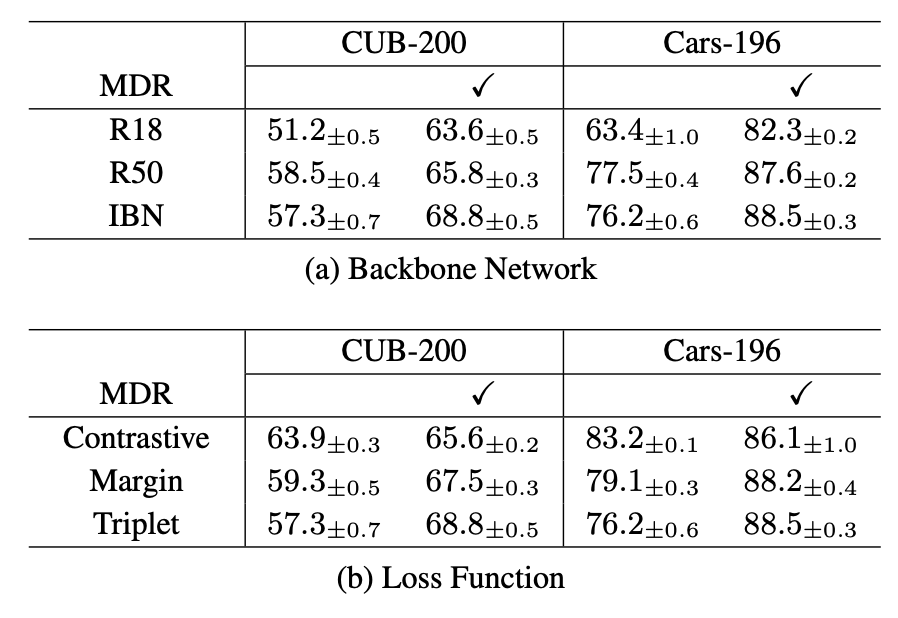
[ Table 2 ] Recall@1 comparison with various backbone net- works, loss functions, and level configurations. The models of (a) are trained with Triplet loss. The models of (b) use IBN as the backbone network. In (a) and (b), a column with ✓ indicates that the models are trained with MDR.
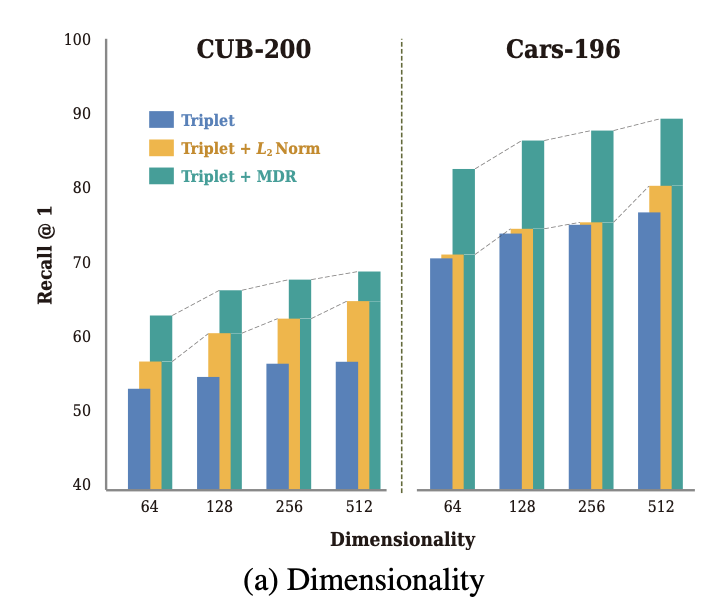
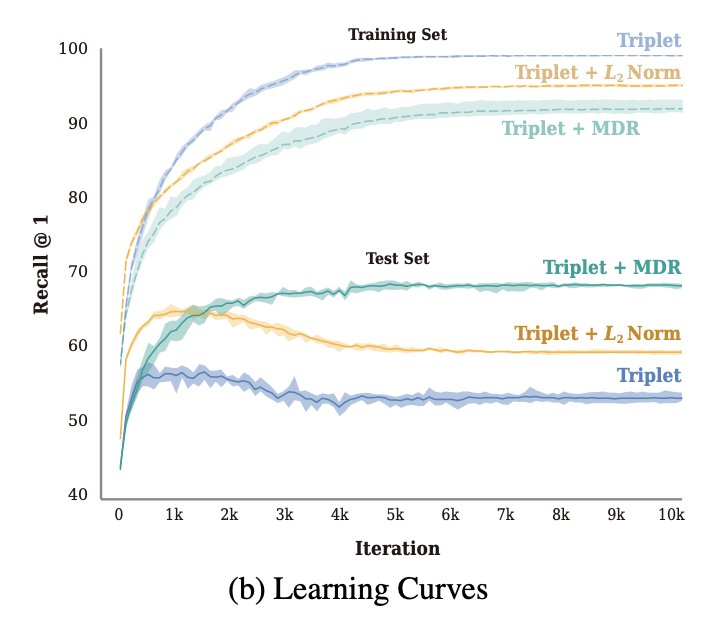
[ Figure 4 ] (a) compares the three methods on various dimensionalities of the embedding vector on CUB-200 and Cars- 196. (b) shows the learning curves of the three methods for the training and test set on CUB-200.
Footnotes
-
정규화는 모델의 설명력을 높이면서도 복잡도를 줄이는 기법을 가리킨다. 정규화 방법론 중 하나인 L2 정규화는 학습 데이터에 따라 특정 가중치의 값이 지나치게 커지는 걸 방지하도록 한다. ↩
-
훈련 데이터에 대한 손실(함수)값이 감소한다고 해서 학습하지 않은 새로운 데이터에서도 같은 정확도를 낸다는 보장은 없다. 이처럼 훈련 데이터에 대해서만 좋은 결과를 내는 현상을 과적합이라고 표현한다. 훈련 데이터에 포함된 노이즈noise마저 버린 상태로, 훈련 데이터가 적을수록 과적합 정도는 심해진다. ↩
-
손실값이 작아서 실제 가중치 업데이트에 미비한 영향을 미치는 샘플 ↩
-
손실값이 커서 가중치 업데이트에서 지배적인 영향을 미치는 샘플 ↩