NLP
RYANSQL: Recursively Applying Sketch-based Slot Fillings for Complex Text-to-SQL in Cross-Domain Databases
최동현(카카오엔터프라이즈), 신명철(카카오엔터프라이즈), 김응균(카카오엔터프라이즈), 신동렬(성균관대학교)Computational Linguistics
2021-03-26
스파이더 챌린지SPIDER Text-to-SQL Challenge 성과를 정리한 공동 연구 논문이 Computational Linguistics에 실렸습니다. 미국 예일대학교에서 주최한 스파이더 챌린지는 각종 데이터를 정리∙보관할 때 사용하는 데이터베이스와 자연어 형태의 사용자 질의가 주어졌을때, 이 질의문을 SQLStructured Query Language1문으로 변환해주는 Text-to-SQL2 알고리즘의 정확도를 평가합니다.
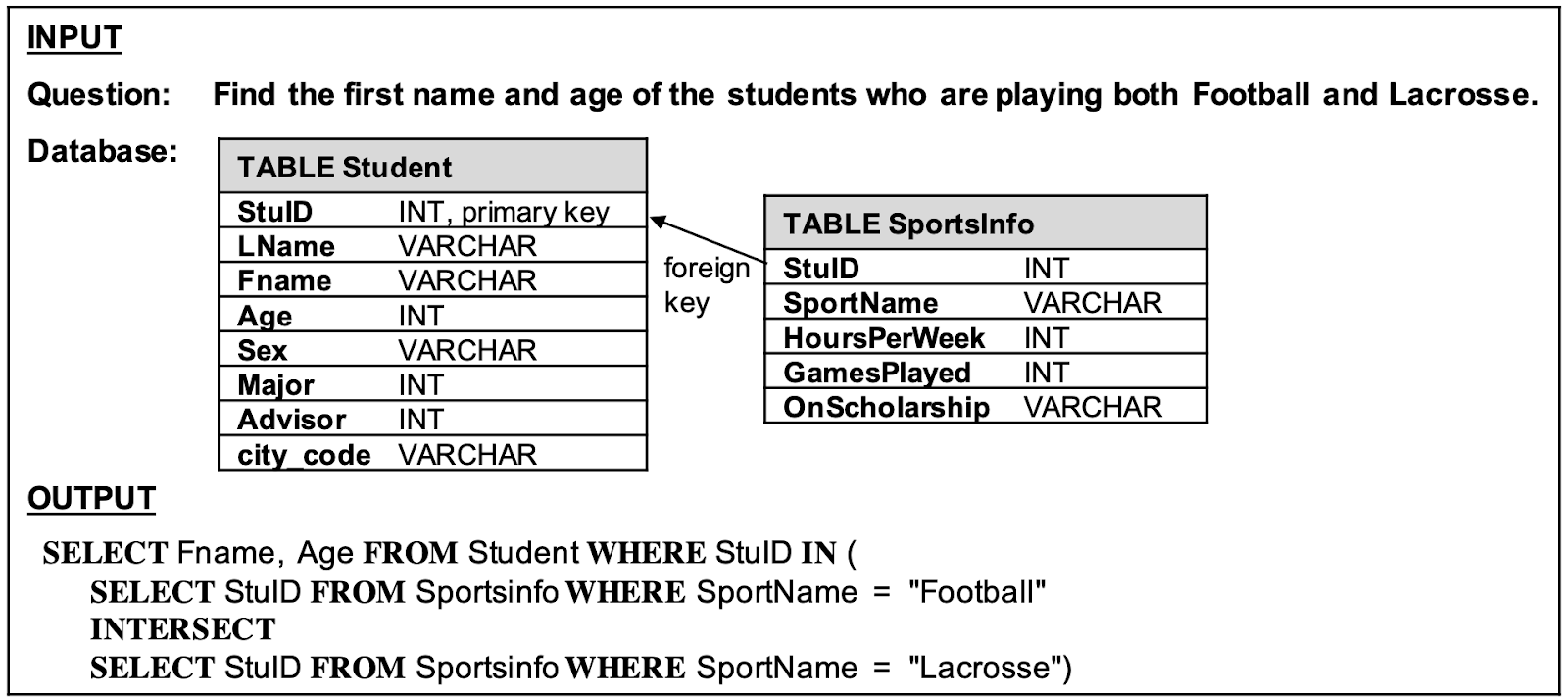
[ 표 1 ] 주어진 자연어 문장과 데이터베이스를 이용해 SQL 문을 생성하는 예시
자연어 질의문을 SQL 문으로 변환하는 데에는 스케치 기반 슬롯 채우기sketch-based Slot Filling가 주로 활용돼 왔습니다. SELECT3 문에 몇 개의 열column을 입력해야 하는지, 어떤 열을 선택해야 하는지, 집계 함수aggregator4로 무엇을 써야 하는지 등 판별해야 할 정보slot를 먼저 구분하고 나서, 각 정보의 값을 채워넣는 식입니다. 다만 이 방식으로는 쿼리 속에 또 다른 쿼리가 든 중첩 질의nested query를 생성하는 데 한계가 있습니다. SELECT 문의 개수가 정해지지 않아서 전체 설계도 자체를 그릴 수 없기 때문입니다.
공동 연구팀이 제안한 Text-to-SQL 알고리즘인 RYQNSQLRecursively Yielding Annotation Network for SQL은 대규모 영어 비라벨링 말뭉치를 사전학습한 언어 모델인 BERT에 자체 고안한 SPCStatement Position Code 기법을 적용했습니다. SPC는 슬롯을 채울 때 중첩된 SELECT문을 좀 더 정확하게 생성할 수 있도록 합니다. 실험 결과, 스파이더 벤치마크 데이터셋에 대해 현재 최고 성능의(SOTA)5 모델보다 3.2%p 더 높은 58.2%의 정확도를 달성했습니다.
카카오엔터프라이즈는 데이터의 스키마(테이블 이름, 열 이름)뿐만 아니라 실제 값도 활용하는 방식 등으로 자사 Text-to-SQL 알고리즘의 성능과 사용성을 높여 기업 데이터베이스 활용의 문턱을 낮추는 데 기여할 계획입니다.
Overall Architecture
Figure 1 shows the overall network architecture of the input encoder. The input encoder consists of five layers: Embedding layer, Embedding Encoder layer, Question-Column Alignment layer, Table Encoder layer, and Question-Table Alignment layer. Table 1 shows the proposed sketch for a SELECT statement. The sketch-based slot-filling decoder predicts values for slots of the proposed sketch, as well as the number of slots.
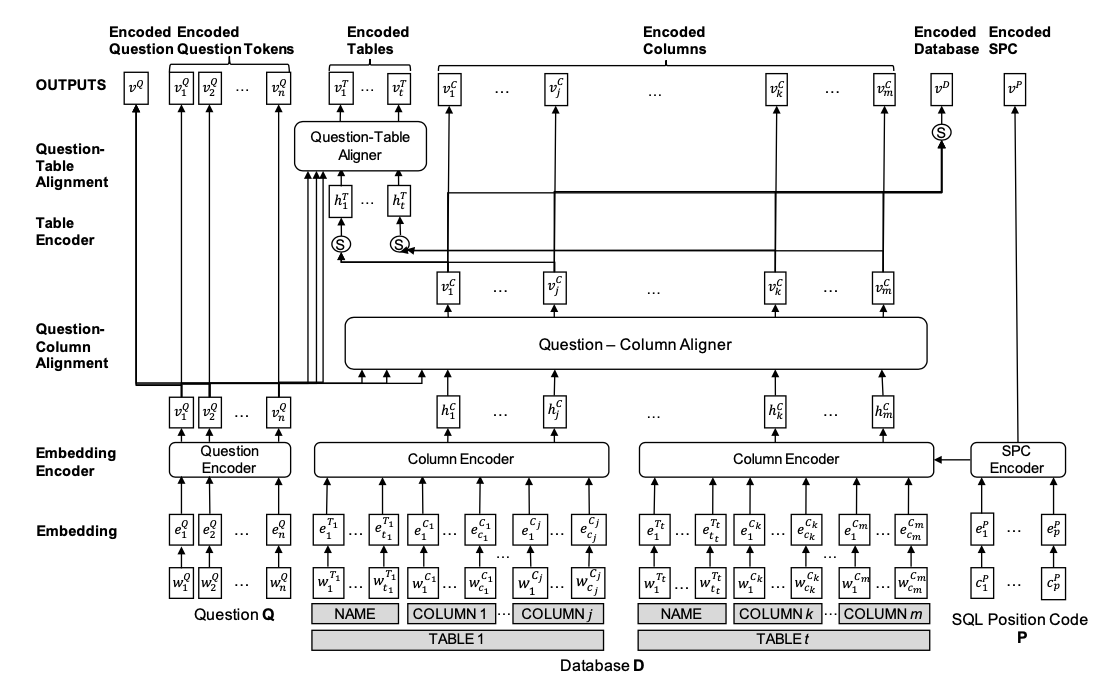
[ Figure 1 ] Network architecture of the proposed input encoder. S represents self-attention.
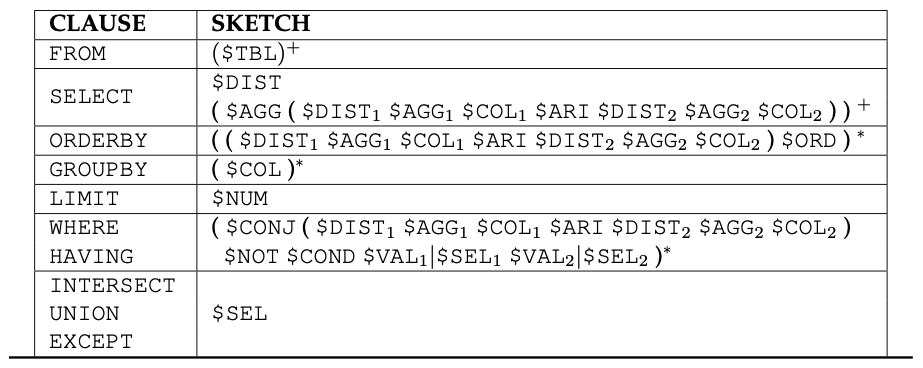
[ table 1 ] Proposed sketch for a SELECT statement. $TBL and $COL represent a table and a column, respectively. $AGG is one of {none, max, min, count, sum, avg}, $ARI is one of the arithmetic operators {none, -, +, *, / }, and $COND is one of the conditional operators {between, =, >, <, >=, <=, !=, in, like, is, exists}. $DIST and $NOT are boolean variables representing the existence of keywords DISTINCT and NOT, respectively. $ORD is a binary value for keywords ASC/DESC, and $CONJ is one of conjunctions {AND, OR}. $VAL is the value for WHERE/HAVING condition; $SEL represents the slot for another SELECT statement.
Experiments
Table 2 shows that the proposed system RYANSQL improves the previous sketch-based slot filling system RCSQL by a large margin of 15% on the dev set. Note that the RCSQL fine-tuned another well known pretrained language model ELMo. With the use of BERT, among the systems without database content, the proposed systems (RYANSQL + BERT and RYANSQL v2 + BERT) outperforms the previous state-of-the-art by 2.5% and 4.9% respectively on the hidden test dataset. The proposed system still shows competitive results compared to the systems using database content; RATSQL v3 + BERT outperforms the proposed system by better aligning user questions and database schemas using database content.

[ Table 2 ] Evaluation results of the proposed systems and other state-of-the-art systems.
We evaluated the proposed models on the CSpider dataset. CSpider is a chinese-translated version of the Spider benchmark. Only the question of the spider dataset is translated; database table names and column names remain as English. Evaluation on the CSpider dataset will show if the proposed model could be applied on the different languages, even when the question language and database schema language are different. To handle the case, we used multilingual BERT, which has the same network architecture with BERT-base but is trained using multilingual corpus.
The results are shown in Table 3. Compared to the exact matching accuracy 51.4% of RYANSQL + BERT-base on Spider dataset, the multilingual version shows 10% lower accuracy on dev set, but still shows comparable results to other state-of-the-art systems which are designed for CSpider dataset. Our proposed system showed 34.7% test accuracy on the test set, and ranked at 2nd place on the leaderboard.

[ Table 3 ] Evaluation results on CSpider dataset with other state-of-the-art systems.