SPEECH/AUDIO
Glow-TTS: A Generative Flow for Text-to-Speech via Monotonic Alignment Search
김재현(카카오엔터프라이즈), 김성원(서울대학교), 공정일(카카오엔터프라이즈), 윤성로(서울대학교)Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) Oral
2020-12-15
FastSpeech와 ParaNet 같은 최신 TTS(음성합성) 모델은 발화를 병렬적으로 합성non-Autoregressive해 그 속도를 높인 새로운 보코더vocoder를 제안했습니다. 하지만 이런 병렬 모델이 텍스트를 구성하는 음소 순서대로 오디오를 정렬하기 위해서는 따로 훈련된 Autoregressive 모델의 지원이 반드시 필요합니다.
이에 카카오엔터프라이즈는 정렬 모델을 따로 구축하지 않고도 이를 보다 정확하게 추정하는 새로운 TTS 모델인 Glow-TTS를 제안했습니다. Glow-TTS는 플로우 기반 생성 모델flow-based generative models과 동적 프로그래밍dynamic programming의 속성을 활용해 입력된 텍스트 순서에 따라 발화를 차례대로 정렬monotonic alignment합니다.
그 결과, 매우 긴 텍스트로 빠르게 합성함은 물론, 서로 다른 강세와 억양을 갖춘 발화를 생성할 수 있습니다. 자체 실험에서 Glow-TTS는 autoregressive 모델인 Tacotron 2과 비교해 비슷한 품질의 음성을 약 15배 더 빠르게 생성했습니다. 또한 Glow-TTS가 다화자 음성합성 태스크에도 쉽게 적용될 수 있음을 확인했습니다.
카카오엔터프라이즈는 이번 연구로 얻은 기술력과 경험을 바탕으로 E2Eend-to-end TTS 기술을 고도화할 계획입니다.
Abstract
Recently, text-to-speech (TTS) models such as FastSpeech and ParaNet have been proposed to generate mel-spectrograms from text in parallel. Despite the advantage, the parallel TTS models cannot be trained without guidance from autoregressive TTS models as their external aligners. In this work, we propose Glow-TTS, a flow-based generative model for parallel TTS that does not require any external aligner. By combining the properties of flows and dynamic programming, the proposed model searches for the most probable monotonic alignment between text and the latent representation of speech on its own. We demonstrate that enforcing hard monotonic alignments enables robust TTS, which generalizes to long utterances, and employing generative flows enables fast, diverse, and controllable speech synthesis. Glow-TTS obtains an order-of-magnitude speed-up over the autoregressive model, Tacotron 2, at synthesis with comparable speech quality. We further show that our model can be easily extended to a multi-speaker setting.
Overall Architecture
Inspired by the fact that a human reads out text in order, without skipping any words, we design Glow-TTS to generate a mel-spectrogram conditioned on a monotonic and non-skipping alignment between text and speech representations.
By combining the properties of flows and dynamic programming, Glow-TTS efficiently searches for the most probable monotonic alignment between text and the latent representation of speech. The proposed model is directly trained to maximize the log-likelihood of speech with the alignment.
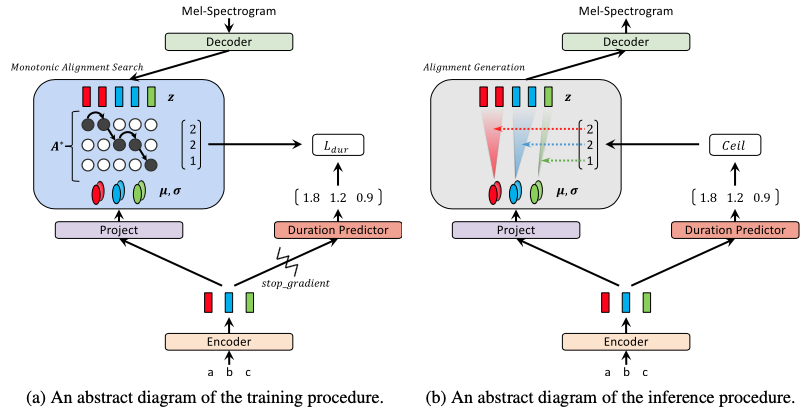
[ Figure 1 ] Training and inference procedures of Glow-TTS
Experiments
We vary the standard deviation (i.e., temperature T ) of the prior distribution at inference; Glow-TTS shows the best performance at the temperature of 0.333. For any temperature, it shows comparable performance to Tacotron 2.

[ Table 1 ] The Mean Opinion Score (MOS) of single speaker TTS models with 95% confidence intervals. On average, Glow-TTS shows a 15.7 times faster synthesis speed than Tacotron 2. The CER(character error rate) of Tacotron 2 starts to grow when the length of input characters exceeds about 260. On the other hand, even though our model has not seen such long texts during training, it shows robustness to long texts.
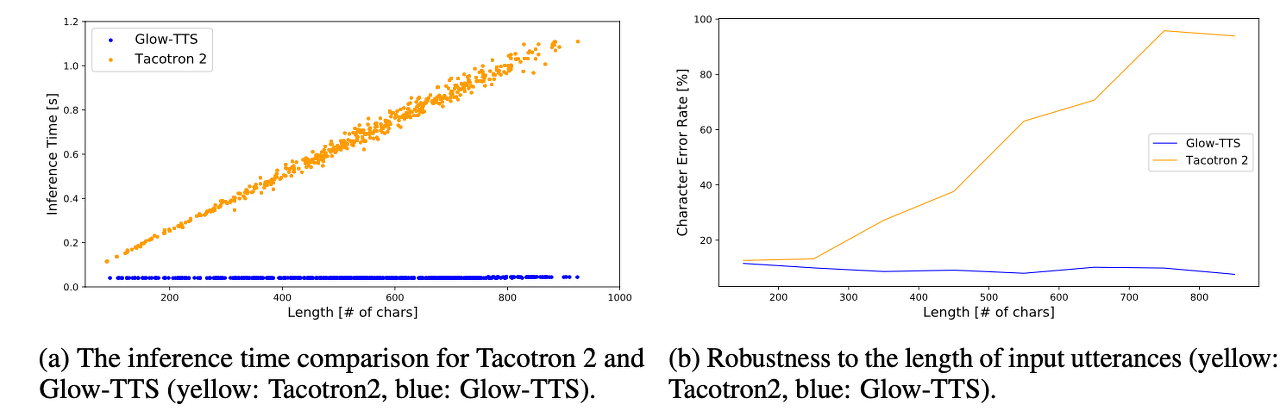
[ Figure 2 ] Comparison of inference time and length robustness