NLP
Reference and Document Aware Semantic Evaluation Methods for Korean Language Summarization
이동엽(카카오), 신명철(카카오엔터프라이즈), 황태선(고려대학교), 조승우(카카오엔터프라이즈), 고병일(카카오엔터프라이즈), 이다니엘(카카오엔터프라이즈), 김응균(카카오엔터프라이즈), 조재춘(한신대학교)International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING)
2020-12-08
공동 연구팀이 제안한 RDASSReference and Document Aware Semantic Evaluation Methods for Korean Language Summarization는 텍스트 요약 모델의 성능을 측정하기 위한 새로운 평가 척도입니다. 기존의 평가 척도인 ROUGE와 비교 실험을 진행한 결과, RDASS는 실제 사람과 유사한 평가 결과를 냈습니다. 또한 공동 연구팀은 정성적 평가를 통해 RDASS가 <모델이 생성한 요약문, 실제 정답 요약문>의 의미적 유사도를 더 잘 반영할 수 있다는 점을 확인했습니다.
공동 연구팀은 영어 텍스트 요약 태스크에서의 추가 검증과 같은 RDASS의 상대적 효용성을 입증하는 실험을 진행하는 한편, 기계가 생성한 요약문의 참 또는 거짓을 판단하는 요소도 반영하는 연구를 진행할 계획입니다.
Abstract
Text summarization refers to the process that generates a shorter form of text from the source document preserving salient information. Recently, many models for text summarization have been proposed. Most of those models were evaluated using recall-oriented understudy for gisting evaluation (ROUGE) scores. However, as ROUGE scores are computed based on n-gram overlap, they do not reflect semantic meaning correspondences between generated and reference summaries. Because Korean is an agglutinative language that combines various morphemes into a word that expresses several meanings, ROUGE is not suitable for Korean summarization. In this paper, we propose evaluation metrics that reflect semantic meanings of a reference summary and the original document, Reference and Document Aware Semantic Score (RDASS). We then propose a method for improving the correlation of the metrics with human judgment. Evaluation results show that the correlation with human judgment is significantly higher for our evaluation metrics than for ROUGE scores.
Methods
To conduct reference and document aware semantic evaluation, we first compute cosine similarity score between the generated summary with the original document s(p,d). Then we compute cosine similarity score between the generated summary with the reference summary s(p,r). Given a reference and source document, the reference-document-aware semantic score (RDASS) of the generated summary is defined by averaging s(p,r) and s(p,d). The reference-document-aware evaluation metric model can be further trained to cap-ture more contextualized information from both on reference summary and document.
Experiments
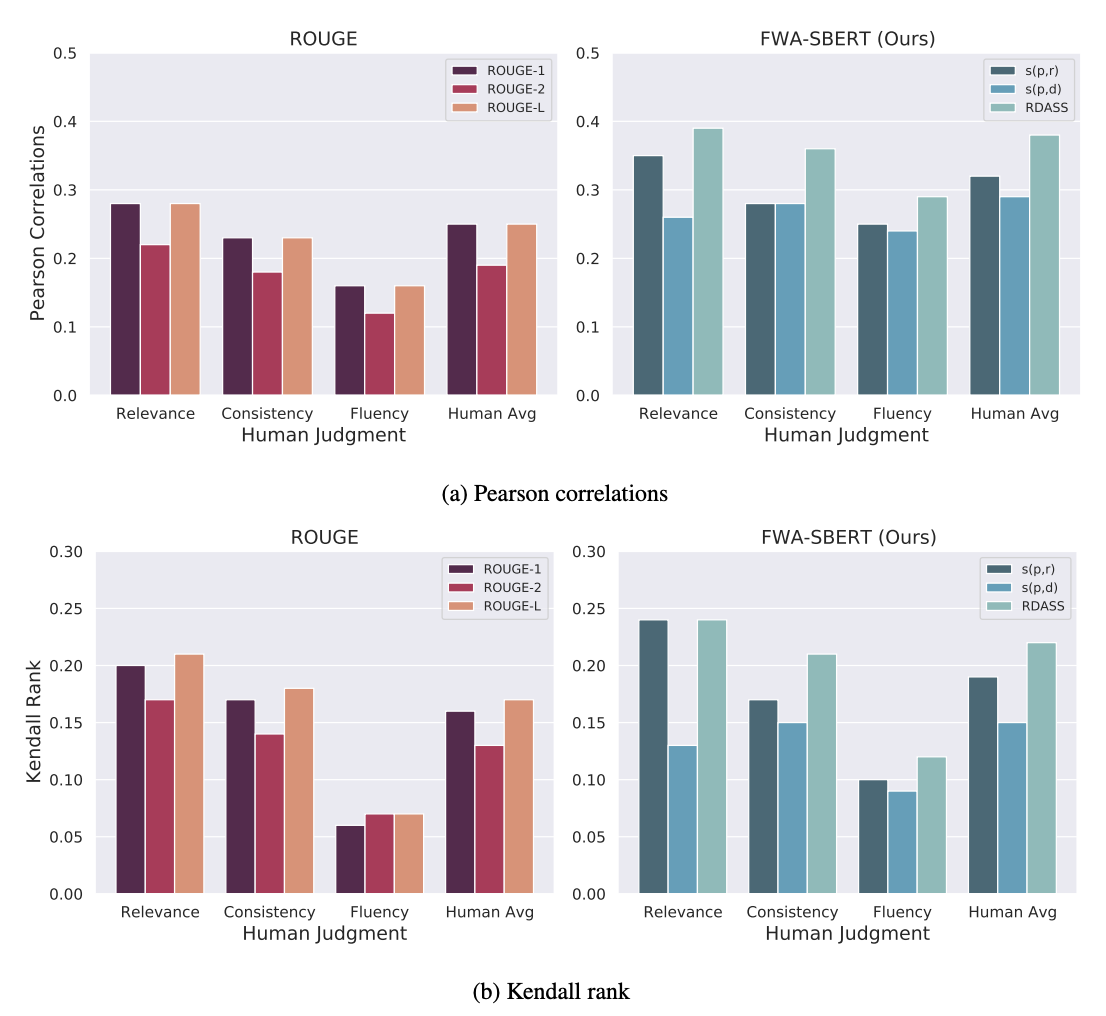
[ Figure 1 ] Pearson correlations and Kendall rank of the proposed evaluation metrics with human judgment
Figures (1a) and (1b) show the Pearson correlation and Kendall rank, respectively, of the proposed evaluation metrics with human judgment on the 200 sampled summaries. Pearson correlation measures whether the two variables are linearly related, where 1 indicates positive linear correlation and -1 indicates negative linear correlation. And Kendall rank measures the rank correlation of the two variables, where 1 indicates two variables are similar and -1 indicates dissimilar. Both correlation measure methods are widely used in summarization tasks to analyze correlation with human judgment. In the Pearson correlation matrix, the correlation with human judgment was significantly higher for the proposed evaluation metrics than for ROUGE scores. Additionally, in the Kendall rank matrix, the proposed evaluation metrics showed highest correlation with human judgment than did the ROUGE scores. Among the proposed evaluation metrics, s(p, r) showed higher performance than s(p, d) and RDASS showed the highest correlation with human judgment. These results indicate that the proposed evaluation metrics can reflect deep semantic meaning overcoming the limitations of ROUGE which based on n-gram overlap.