NLP
Revisiting modularized multilingual NMT to meet industrial demands
류성원(카카오엔터프라이즈), 손보경(카카오엔터프라이즈, 서울대), 양기창(카카오엔터프라이즈, 숭실대), 배재경(카카오엔터프라이즈)Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP)
2020-11-16
카카오엔터프라이즈는 M2NMTModularized Multilingual Neural Machine Translation Model1의 가치를 재발견했습니다. 여러 번역 조건에서 성능 저하를 보이는 1-1 MNMT2와는 달리, M2NMT에서는 성능이 유지됐습니다. 새로 추가된 언어를 포함한 태스크에서 NMT3보다 좋은 성능을 보일 수 있음을 확인하였습니다. 또한, 제로샷zero-shot4 에서 피벗 방식pivot translation5 보다 더 좋은 성능을 달성했습니다. 카카오엔터프라이즈는 다국어 학습으로 인한 시너지data-diversification, and regularization effect가 주된 요인이라 분석했습니다.
카카오엔터프라이즈는 향후 이 모델이 생성한 ‘언어에 독립적인 특징 공간interlingual space‘의 여러 효용을 검증하는 연구를 진행할 계획입니다.
Abstract
The complete sharing of parameters for multilingual translation (1-1) has been the mainstream approach in current research. However, degraded performance due to the capacity bot- tleneck and low maintainability hinders its extensive adoption in industries. In this study, we revisit the multilingual neural machine translation model that only shares modules among the same languages (M2) as a practical alternative to 1-1 to satisfy industrial requirements. Through comprehensive experiments, we identify the benefits of multi-way training and demonstrate that the M2 can enjoy these benefits without suffering from the capacity bottleneck. Furthermore, the interlingual space of the M2 allows convenient modification of the model. By leveraging trained modules, we find that incrementally added modules exhibit better performance than singly trained models. The zero-shot performance of the added modules is even comparable to supervised models. Our findings suggest that the M2 can be a competent candidate for multilingual translation in industries.
Experiments
By extensively comparing the single models, 1-1 model, and M2 in varying conditions, we find that the M2 can benefit from multi-way training through data-diversification and regularization while suffering less from capacity bottlenecks.
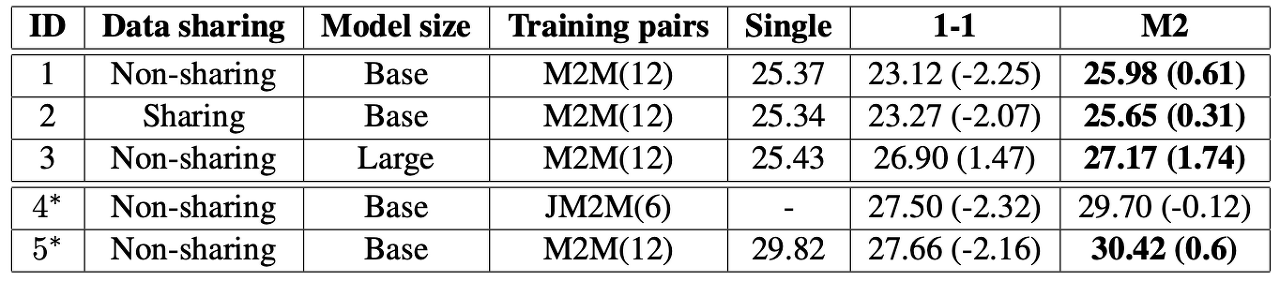
[ Table 1 ] Averaged SacreBLEU test scores of single models, 1-1, and M2 trained using a balanced dataset of different configurations. M2M indicates the training of full many-to-many directions among languages (12 directions), whereas JM2M represents the training of directions that only include English on one side(6 directions). * indicates that the score is averaged only on English-centric.